Get this deal! Call now.
Speak with a vehicle protection plan specialist and get $300 off any new contract instantly.
Call 866-678-4172
or scan the code below
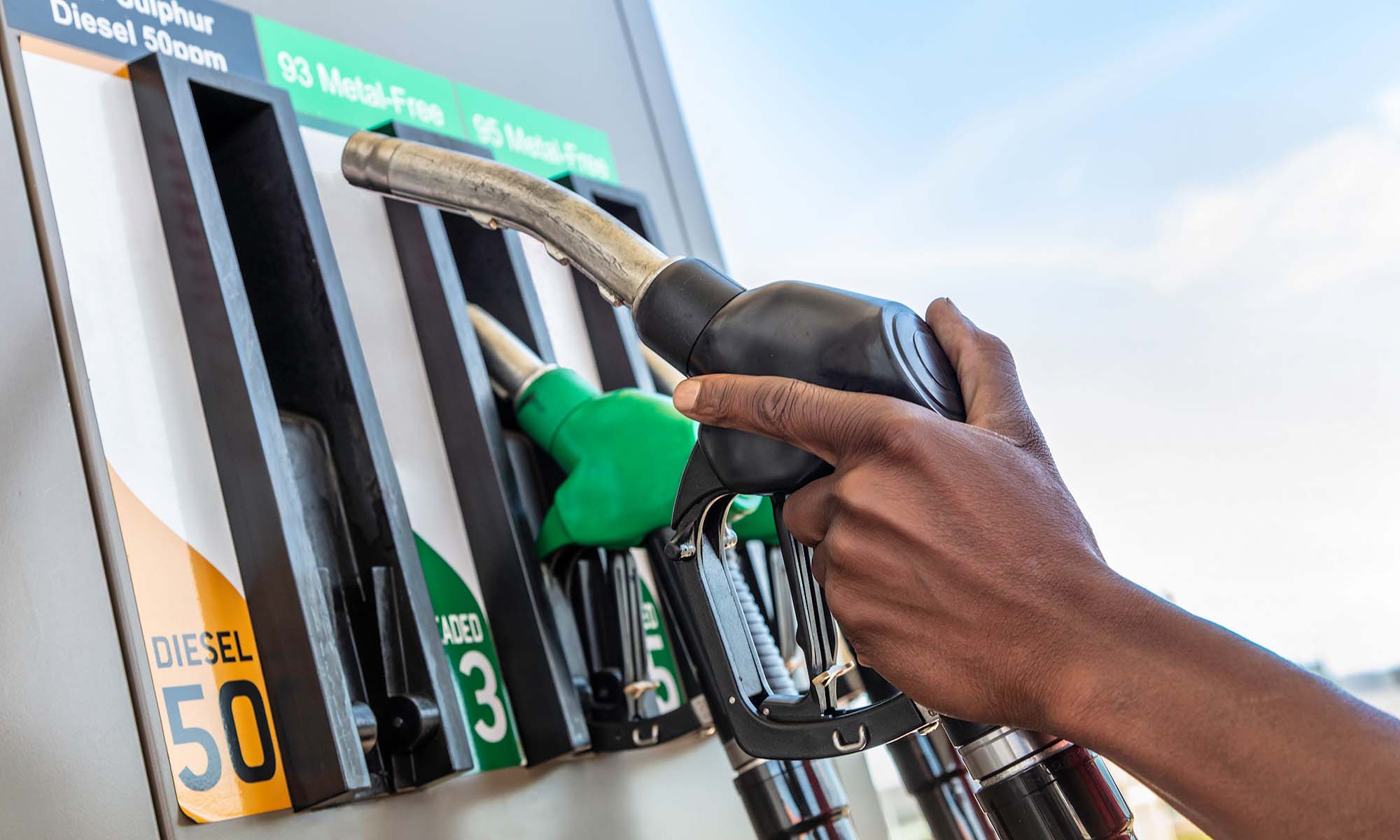


As a car owner, you’ve likely mastered the art of “filling up the tank.” But while it may seem a fairly simple part of car ownership, even the most experienced drivers could be tempted to go with the cheaper option when faced with higher than normal gas prices. However, while you may be saving a few bucks at the gas station, you could be left with thousands of dollars more in car repair bills if you put the wrong fuel in your car.
That’s why understanding more about the different fuel types, like the difference between diesel and gasoline, and understanding what octane ratings you will see filling up, can help you maximize engine performance and save at the pump.
While diesel and gasoline are made by refining crude oil and are used to power machines and motor vehicles, they aren’t interchangeable. First, gasoline is more highly refined, making it thinner and more “vapor-producing.” As a result, gasoline will burn more quickly, which enables it to create more power.
On the other hand, diesel is thicker and evaporates less quickly. This consistency gives diesel a greater energy density and the ability to create about 20% more energy than a comparable amount of gasoline.
These differences are why you’ll see a gasoline engine used where horsepower (hp) and straight-line acceleration are the desired car qualities. In contrast, a diesel engine is favored in applications where low-end torque helps hauling heavy loads or towing hefty trailers, which is why diesel power is the go-to choice for heavy-duty trucks and big rigs.
European inventor Rudolph Diesel invented his namesake engine in the late 1800s. His efforts came about from a search for more-efficient alternatives to the steam engines of the day. Diesel fuel (although it wasn’t yet called “diesel”) was a byproduct of kerosene distillation that began in the mid-1850s. Diesel discovered the energy-dense surplus fuel was ideal for his “powerplant,” aka the engine.
As for how it works, a diesel engine doesn’t rely on spark plugs for ignition like a gas engine. Instead, it’s an internal combustion engine that uses a combustion chamber where the fuel is vaporized and ignited at a high temperature by compressed air, resulting in a higher compression ratio than a normal gas-powered engine. And this high-compression combustion process, along with energy-dense fuel, allows diesel vehicles to be more fuel efficient than gas engines.
For example, the 2023 Chevrolet Silverado 1500 Crew Cab (rear-wheel drive) has an available three-liter, turbocharged six-cylinder diesel engine with an EPA estimated 23 miles per gallon (mpg) city and 31 mpg highway. The same vehicle with a gas-powered V8 is rated for 14 mpg city and 18 mpg highway. That’s a major difference. Even the Silverado with a gas-run turbocharged four-cylinder engine gets just 19 mpg city and 22 mpg highway. You’ll also get the same 460 pounds per feet (lb-ft) of torque in the diesel engine as the V8, but while you’ll save at the pump and have the same torque, you’ll be lacking in overall horsepower, as you’ll only get around 277 compared to the V8’s 420 hp.
But along with diesel engines in pickup trucks and even some SUVs, you’ll also see them used in “beast of burden” vehicles such as tractors, large trucks, delivery vans, and school buses. You may also hear a lot more about biodiesel, a type of fuel made out of (believe it or not) animal fats, vegetable oils, and even grease that’s been recycled from restaurants, especially with the push to produce greener vehicles with fewer emissions. However, while biodiesel produces fewer air pollutants and is biodegradable, you will find it is much more expensive than gas or diesel fuel. Biodiesel will also have you filling up the “gas tank” more often as it provides less power and a lower fuel economy than other fuel types.
Like diesel engines, gasoline engines are also internal combustion engines. However, gasoline, which also came about as a byproduct of the kerosene distillation process, is the main source of this combustion process. However, while gasoline is widely used worldwide, it wasn’t as popular when first discovered. Instead, it wasn’t until the rise of the automobile at the turn of the 20th century did it start to become more prevalent.
As for how it works, a gas engine gets its power from a compressed fuel mixture that is ignited by a spark (generated by a spark plug). The resulting combustion moves the piston, which rotates the crankshaft and powers the car. Unlike diesel engines, this process generates more energy, which is why a gas engine is best for top-end horsepower. For this reason, you won’t find a diesel engine in a NASCAR racer or an everyday sports car.
However, like the differences between gasoline and diesel, you’ll also find different types of gas, often separated by octane ratings.
Today, you’re very unlikely to find a gas pump with less than three choices for gasoline: regular, mid-grade, and premium gas. These are simplified terms for the different octane ratings for gasoline. You’ll also see a pair of numbers on individual gas pumps that more precisely spell out octane ratings: 87 (regular), 89 (midgrade), and 91 or 93 (premium), though some brands offer higher-octane gas. But what do these labels and numbers mean?
These are all ways to categorize gasoline’s octane rating, determining how much compression a fuel can take before igniting. In simpler terms, the higher the octane rating, the less likely it will pre-ignite and damage the engine. Most premium and high-performance cars use high-compression engines to maximize power, requiring high-octane gasoline to operate correctly. This can also help you get better fuel economy and t improve your car’s emissions.
But, high-octane fuel doesn’t directly increase engine output. So, putting premium gas in a car that only needs regular gas is a waste of money. You may also see that some vehicles have a premium fuel recommendation but can operate with a lower octane fuel (yet with slightly less horsepower). Still, while possible, it’s always best to use the correct octane gasoline suggested in your car’s owner’s manual as you could potentially risk damaging your engine. To give you some idea of the type of gasoline recommended for some vehicles, here are a few 2022 model year examples, according to fueleconomy.gov:
You’ll often see luxury or sportscars use high-octane gasoline to maximize performance. This requires more sophisticated engineering, which is tied to their often higher prices.
With the differences between fuel types, like diesel and gasoline, or even the differences between octane ratings, it can be absolutely vital that you fill up with the recommended fuel for your vehicle. That’s why many gas stations label the nozzles with their respective octane ratings and will also often color-code them to indicate fuel type to help ensure you don’t fill up with the wrong gas:
Understanding the difference between gasoline and diesel also involves looking at fuel pump nozzles. For instance, the diameter of the diesel pump nozzle is slightly larger than a gas nozzle, which prevents accidentally adding diesel fuel to a gas-powered car. So, doing so would require a deliberate act or adding fuel from an unmarked container (something to never do). And filling a gas car with diesel will soon lead to a breakdown, as the thicker fuel will foul the injectors and lines. The remedy is a time-consuming and pricey fuel system flush.
However, filling a diesel vehicle with gasoline is still possible but will result in severe engine problems. Adding gasoline changes the flash point of diesel fuel, which causes premature ignition and engine damage to any diesel car. The fuel pump and diesel fuel injectors are also affected.
Buying the wrong fuel can also involve selecting the incorrect octane for a gas-powered car. Many vehicles that require more expensive gas can function on regular gas but will not run at peak performance. However, engines that can only run on premium fuel may be damaged by using a lower octane fuel. Review the owner’s manual to confirm your car’s requirements and learn what to do if lower-grade gas has found its way into the fuel tank. Also, remember that a handful of vehicles mandate mid-grade or better gas, so be sure to learn what to do if regular fuel is used with one of these if you happen to own one. However, it‘s not an issue if the vehicle uses regular gas; you’ll just have spent money on unneeded mid-grade or premium fuel.
Knowing the differences between gasoline and diesel fuel can help you be better equipped as a car owner. After all, accidentally putting the wrong type of fuel in the gas tank can potentially result in thousands of dollars in repair bills. But will being diligent on the type of gas you put in your vehicle, even the most well-maintained ones can break down, regardless of the type of engine they have. And when that happens, and you’re out of your factory warranty coverage, you’d be left paying for any unexpected and expensive automotive repair bills on your own. This is when an Endurance vehicle protection plan can make a difference.
With coverage beginning at $79 per month, Endurance provides peace of mind against the unexpected for a car’s vital components, like the engine and transmission. There are plans for almost every vehicle on the road, including high-mileage cars and select luxury models. Plus, every Endurance customer enjoys flexible payment options, a 30-day money-back guarantee, and the ability to choose any ASE Certified mechanic. Other benefits include 24/7 roadside assistance, rental car coverage, and trip interruption protection regardless of your coverage. You can also take advantage of a full year of free Elite Benefits, including extra perks and savings like tire repairs and replacements, key fob replacements, and more.
Don’t wait until you’re left dealing with an unexpected and expensive repair; protect your vehicle today by requesting a free, no-obligation online quote or calling (800) 253-8203 to speak with an award-winning Endurance customer care team member. Check out the Endurance blog for expert-written information on car care, DIY maintenance, vehicle reviews, and other essential topics.

We're here to make sure you get the most comprehensive EV protection. That's why we've partnered with Xcelerate Auto to offer you transparent and dependable Tesla coverage.
Want us to contact you about XCare coverage for your Tesla?



Call for $300 off any new plan!
By clicking the button, you consent to Endurance using automated technology to call, email, and text you using the contact info above, including your wireless number, if provided, regarding auto protection or, in California, mechanical breakdown insurance. You also agree to the Endurance Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions. Consent is not a condition of purchase, and you can withdraw consent at any time. Message and data rates may apply.
Speak with a vehicle protection plan specialist and get $300 off any new contract instantly.
Call 866-678-4172
or scan the code below


Simply fill out the information below and we will follow up fast with your free no-obligation quote.
By clicking the button, you consent to Endurance using automated technology to call, email, and text you using the contact info above, including your wireless number, if provided, regarding auto protection or, in California, mechanical breakdown insurance. You also agree to the Endurance Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions. Consent is not a condition of purchase, and you can withdraw consent at any time. Message and data rates may apply.

To speak to a vehicle protection plan specialist and save $300
Scan the code below
Larry Witherspoon Jr. is a co-founder and Executive Director of the Automotive Training Center. Larry has held multiple leadership positions in the U. S. Navy and with various Fortune 100 companies. In addition to his business experience, Larry grew up understanding the difficulties all young men face becoming adults especially those that come from challenging circumstances. He has taken those experiences growing up and combined them with his passion for vehicles to start the Automotive Training Center. Read more about Larry.